Phases

Phases are the appearance of the illuminated surface of a moon or planet as seen from earth and are not the same as eclipses. The boundary between the dark and sunlit hemispheres of an object is known as the terminator. The rotation of the object makes this terminator change positions in relation to its surface. The boundary which a point on the surface crosses to come into the sunlit portion is called the sunrise terminator. The other side is called the sunset terminator. Because every planet and moon in the solar system shines by reflecting the sun’s light, the illuminated surface of an object is usually not the same shape as the object. The moon is the object with the most obvious phases, but the planets also have phases. Only the moon and the two inferior planets can have phases which show half or less of their surfaces. The superior planets always have at least half of their surfaces lit as seen from earth. Because the phases of the moon are visible to the naked eye, the moon will be used to explain the different types of phases.
Lunar Phases
The phases of the moon are called lunar phases. At opposition, the near side of the moon is fully lit. As the moon continues to revolve around the earth, the near side of the moon starts to become less and less illuminated until it reaches conjunction, when the near side is no longer illuminated. The moon’s near side then starts to become more and more illuminated until it again reaches opposition. The time the moon takes from opposition to opposition is known as the synodic month.
A full moon occurs when the near side of the moon is fully lit. When this happens, the moon is at opposition.
A new moon occurs when the near side of the moon is completely dark. This happens when the moon is at conjunction.
A quarter is when the moon is half lit, also called half full. This occurs both times in the synodic month when the moon is at quadrature. The first quarter occurs when the moon is waxing and is at quadrature. The last quarter occurs when the moon is waning and is at quadrature.
A gibbous moon is when the moon is between full and half full. A gibbous moon can either be waning or waxing.
A crescent moon is when the moon is between new and half full. A crescent moon can either be waning or waxing.
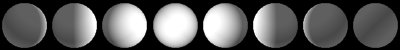
The different types of phases are illustrated below.
|
| Figure 1: The phases of the moon. Counterclockwise from bottom right in top image and from left to right in bottom image they are: waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full, waning gibbous, last quarter, waning crescent, new. |
If you do not see frames, click here to go to the frames page.
If you do not want to use frames, click here to go to the non-frames home page
and sitemap.