 |
| The Solar System Montage. Taken by Various Insturments. Pluto is not shown. Courtesy: NASA/JPL/Caltech |
The Solar System
 |
| The Solar System Montage. Taken by Various Insturments. Pluto is not shown. Courtesy: NASA/JPL/Caltech |
The solar system is the name given to the sun and all of the objects which orbit around it. This includes the major and minor planets, meteoroids, comets, interplanetary dust, and moons. 99.86% of the mass of the solar system is contained in the sun; most of the rest is contained in the planet Jupiter. Two pictures of the solar system are inlcuded below.
 |
| Figure 1: The inner planets. |
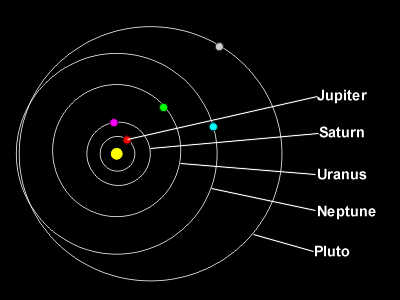 |
| Figure 2: The outer planets. |
The solar system contains nine known major planets, the earth being the third from the sun. Planets which have diameters significantly larger than 1003 km are called major planets. The major planets are the nine main planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. The major planets are grouped into several different categories. The planets closer to the sun than earth are called inferior planets. There are two inferior planets: Mercury and Venus. The planets farther away from the sun than earth are called superior planets. There are six known superior planets: Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto.
Some astronomers also call the four planets closest to the sun terrestrial, or earth-like, planets; this includes Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The giant planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Pluto is included in neither the terrestrial or giant categories. The nine major planets are usually in this order out from the sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. However, because of Pluto’s very eccentric orbit, Neptune is sometimes the outermost planet. Between 1979 and 1999, Pluto was closer to the sun than Neptune.
 |
| Asteroid Ida and its Moon. Courtesy: NASA/JPL/Caltech |
The minor planets are the smaller solar system objects such as asteroids and planetoids. The sizes of minor planets range from 1003 km (the diameter of Ceres, the first of these objects to be discovered) to smaller than 1 km. When the orbit of a minor planet has been calculated, the object is given a minor planet number and a name. The name is usually chosen by the discoverer. Most minor planets orbit the sun in the asteroid belt, which is at a distance of 2 to 3.3 AU on a plane close to the plane of the ecliptic. The objects in the asteroid belt orbit the sun in a direct motion. Minor planets typically have an orbit which is more eccentric than those of major planets.
Meteoroids are objects which are smaller than minor planets. The majority of these objects follow a slightly inclined orbit around the sun. When a meteoroid enters the earth’s atmosphere, it is called a meteor. If a meteoroid hits the surface of the earth, it is called a meteorite. Groups of meteoroids enter the earth’s atmosphere several times each year. These are called meteor showers.
Comets are large objects which have very eccentric orbits around the sun. These objects have three parts, the nucleus, the coma, and the comet trail. The nucleus is the main part of the comet and the only permanent part. It is thought to be made up of 75% ice, mainly water ice, and 25% dust. The nucleus of a comet is often described as a "dirty snowball". The second part, the coma, is a luminous cloud of gas and dust surrounding the nucleus. The shape of comas are usually circular. The third part of a comet, which not all comets have, is the tail. The tail only appears when the comet nears the sun and is a long trail of luminous gas and dust which is pulled out from the nucleus by solar wind. A comet tail always points away from the sun.
For more information, go to:
If you do not see frames, click here to go to the frames page.
If you do not want to use frames, click here to go to the non-frames home page
and sitemap.